By Tynan Heller, Senior Product Manager, Genasys Inc.
Managing disasters isn’t one size fits all. Hurricanes, floods, and wildfires each bring unique challenges. Tackling these emergencies effectively requires tailored strategies and tools. Intelligent zoning has become a game-changer for emergency managers. By turning static data into functional zones, it speeds up decision-making and public alerts. But there’s a catch: different disasters require different zones. This makes the ability to integrate additional data into zones essential for true all-hazard readiness.
Understanding Effective Zoning
What is a Zone?
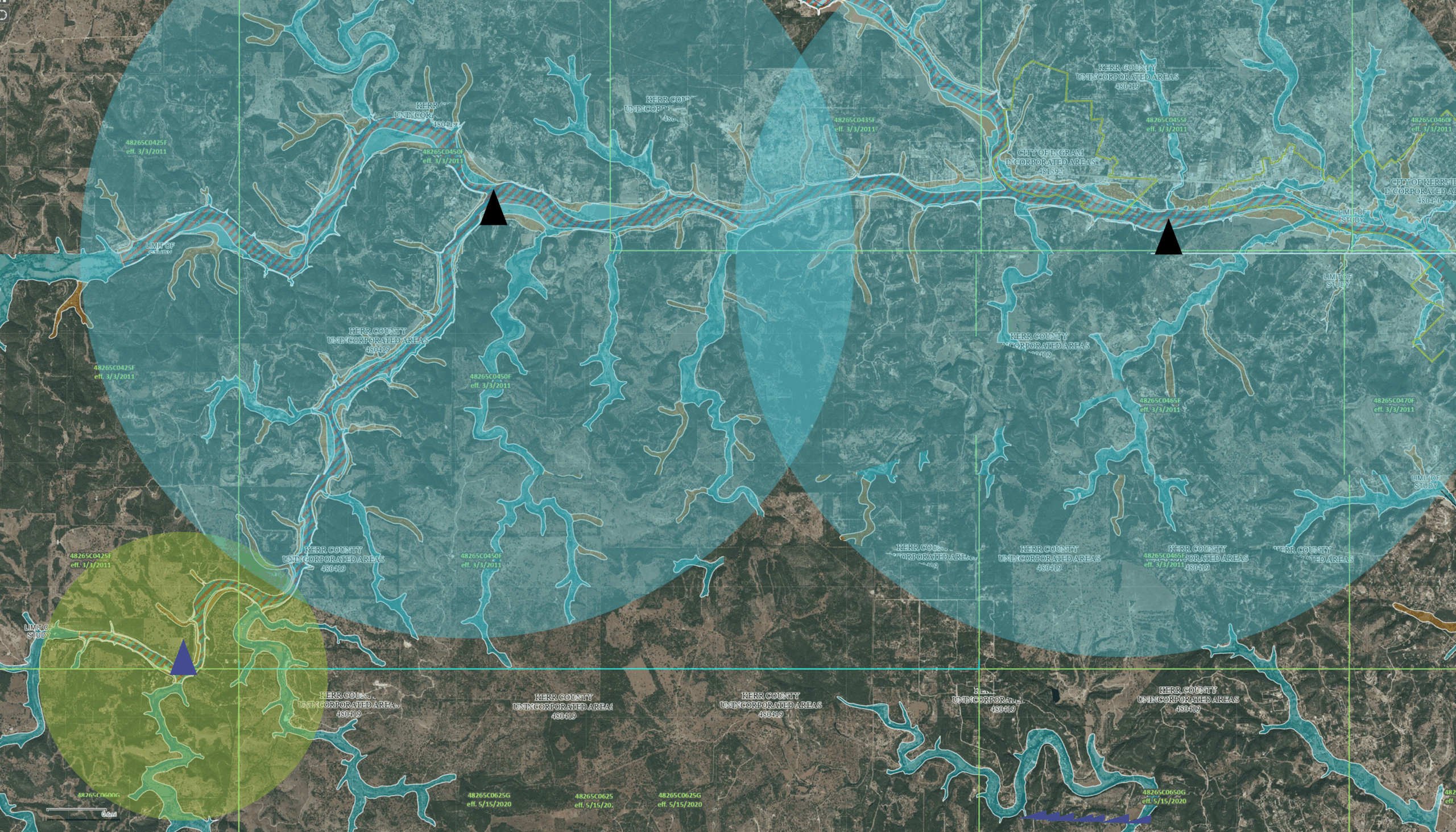
In a way, zones are the evolution of traditional GIS layers. A zone is a geographically defined area designed for targeted emergency response and alerting through an emergency communications solution. Unlike GIS layers, which are static geographic data representations that provide information but require additional steps to become actionable, zones are functional. They allow emergency managers to instantly send alerts, coordinate evacuations, and manage responses within their boundaries.
A zone’s geographic area is defined utilizing aggregated data sources, as well as knowledge and context from local officials. Different disasters require differing data sourcing and need individual consideration of criteria. An effective zone will also include situational awareness information like shelter locations, vulnerable infrastructure, population/vehicle counts during the day and night, alert status, and evacuation instructions.
Now, the latest innovations allow users to integrate GIS data, models, and simulations to modify zones into intelligent custom zones. These intelligent custom zones essentially change to cater to the specific conditions and response needs of their users. This evolution allows responders to not only visualize critical data but also adjust their zones dynamically to improve decision-making and response effectiveness based on their region’s needs.
The Differences Between Disaster Zones
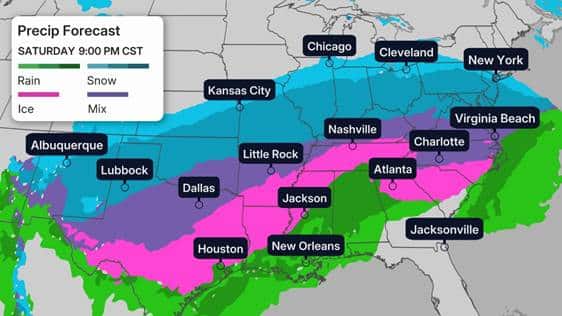
Hurricane Zones: Hurricane zones prioritize storm surge risks and high-wind areas. They tend to be far larger than other disaster zones given hurricanes impact massive areas simultaneously. These zones guide evacuations by focusing on vulnerable coastal areas and inland routes to safety.
Flood Zones: Flood zones consider elevation and water flow paths. They help identify areas at risk of inundation and pinpoint safe shelters on higher ground.
Fire Zones: Fire zones focus on proximity to fuel sources, natural/manmade fire breaks, population density, and escape routes. They highlight areas of vulnerable population and direct residents to safe exits.
The Key to All-Hazard Readiness: Data Integration
No software solution has built-in zones for every disaster type, making a flexible system critical. The ability to import and use data and models from multiple sources in one platform ensures emergency managers are prepared for any situation.
This flexibility transforms response planning. Emergency managers no longer waste time juggling systems or creating zones from scratch. Instead, they act fast, with confidence that their decisions align with real-world conditions. A primary example of efficiency is when ESRI data is integrated it automatically updates zones based on any future changes. Meaning, if the ESRI data is updated the zones will also update.
Why Every Region Needs Multiple Zones
Much of the U.S. are now faced with developing resiliency plans for a multitude of hazard types. While the U.S. West Coast battles wildfires they must consider the risk of floods. The East Coast has traditionally focused on hurricanes and flooding, however, wildfires are now a growing concern. As climate patterns shift, regions are encountering new and more intense hazards. Having zones prepared for these risks increases the protection of the community.
All-Hazard Readiness – A Necessity
Being ready for everything isn’t a luxury; it’s a necessity. Emergency managers and responders need tools that empower them to act swiftly and decisively, regardless of the disaster type. Intelligent zoning, combined with robust data integration, ensures they can handle any emergency. With the flexible zones in place, responders can protect lives when it matters most.